5.6 Spezielle Matrizen
Für die Beschreibung der Matrix Division beschränken wir uns vorerst auf
quadratische Matrizen (
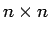 ). Dafür benötigen wir zuerst die
Definition der Einheitsmatrix
). Dafür benötigen wir zuerst die
Definition der Einheitsmatrix
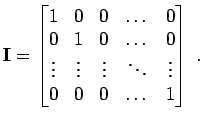 |
(5.27) |
Für die Einheitsmatrix gilt
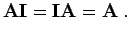 |
(5.28) |
In MATLAB steht für die Erzeugung der Befehl eye
(zB. eye(3)) zur Verfügung.
Die inverse Matrix ist definiert durch
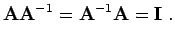 |
(5.29) |
Eine Matrix für die
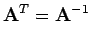 |
(5.30) |
gilt, wird als orthogonale Matrix bezeichnet.
In MATLAB gibt es zur Berechnung der inversen Matrix den Befehl
inv(A).
Winfried Kernbichler
2005-04-26